DP for String Metrics: Longest Common Subsequence
Contents
This articles is about longest common subsequence in a series of articles: DP for String Metrics.
Series: DP for String Metrics
Dynamic programming (DP) solves a complicate problem in optimal substructure by breaking it down into simpler sub-problems, and there are DP patterns that are very effective for string metrics. These articles are my summary notes on them. Please feel free to ping me for anything you think I should add.
- Levenshtein Distance
- Longest Common Subsequence: this article
- Regular Expression
- Distinct Subsequence (coming soon)
- Longest Repeating Subsequence (coming soon)
- Hamming Distance (coming soon)
Longest Common Subsequence
Longest common sequence (LCS) is used for things like fuzzy string searches and diff command. It finds the longest sequence common in (typically) two strings where the common sequence doesn’t need to happen consecutively. E.g. LCS between ABCD and ACBD is 3 (either ABD or ACD.)
DP Table
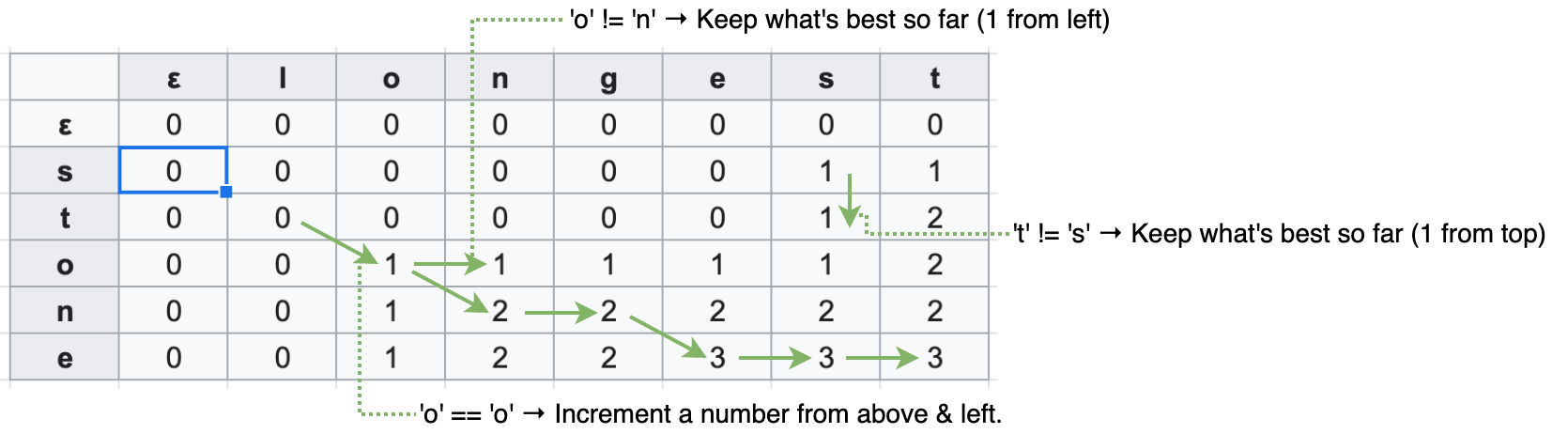
In the table below, “stone” (vertically mapped on left) and “longest” (mapped horizontally on top) are compared. In LCS, we define base cases to be non-character (expressed as ε), so values of the first row and column are all zero.
We go through each cell from position [1, 1] to right every row, comparing each character of two strings. If the characters are identical, we increment a number from left and above by one and update the cell with it. If not, we use the best value up until this point, which is the larger one of either top or left cell. Finally, the cell at the end would be the result count.
Implementation
|
|
Notes
LCS only returns metrics. So if LCS sequence itself is desired instead of metric, we would need another function to retrieve the characters. This can be achieved by using the DP table created in LCS function, tracking the largest numbers from the end and collecting the characters.